The main difference between different flooring materials and their suitability for use with the system is the material’s thermal conductivity or, in other words, how quickly and efficiently heat transfers to the floor surface. The best flooring to use is flooring with good conductivity as it heats up quicker, gives more heat output and is more efficient to run. However, this does not mean that floor heating could not be used under less conductive materials and there are systems available for use with virtually any floor finish. Whether in renovation or new construction, we outline in this article what is needed to know about different floor finishes.
TILE, STONE & POLISHED SCREED
The best type of flooring to use with floor heating is tile and stone. These materials have high thermal conductivity, meaning that the heat transfered from the system reaches the floor surface quickly. Tile and stone also retain heat well, making the system more efficient. Due to the excellent thermal properties, tile and stone are ideal for use with floor heating in high heat loss areas. They can be heated to up to 29°C or more.
The thickness of the tile and stone has little impact on the heat output, but it does increase the heat up time slightly, so a maximum thickness of 20mm is recommended when seeking a highly responsive system.
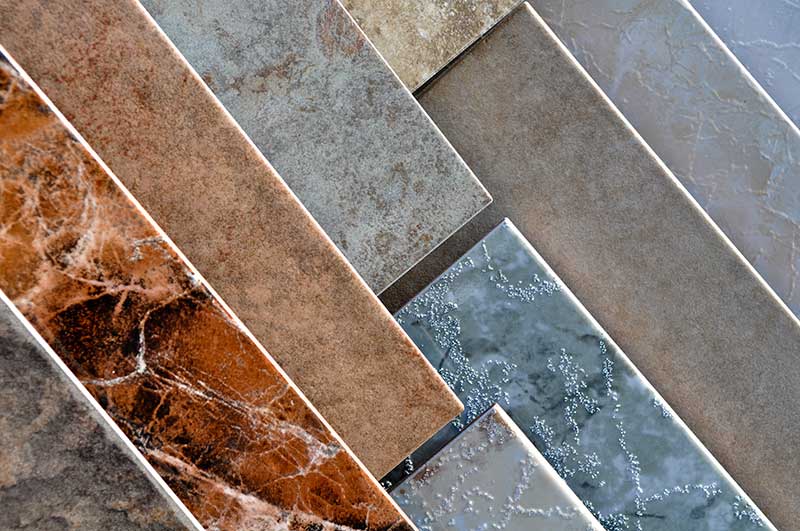

Tile and stone floors are highly conductive making them the best flooring to use with floor heating.
Ceramic andstone tiles
- The best floor material to use with floor heating
- Excellent heat transfer properties and thin profile
- Easy to keep clean
Polished concrete
- Highly conductive allowing fast heat up time
- Suitable for use with electric floor heating systems
Slate and flagstone
- Naturally highly conductive and great with floor heating
- Hard-wearing floor finish ideal for high footfall areas
Marble
- Good thermal conductivity but slower heat up times
Installation tips: floor heating with tile and stone
- Use a quality 2 part flexible tile adhesive when installing floor heating with tiles.
- When installing on a concrete subfloor, always use insulation.
WOOD FLOORING
Different types of wood flooring have different thermal properties, as such there are differences in their suitability for use with floor heating systems. The more dense and the thinner the floor boards are, the better they conduct heat and typically more suitable they are for use with floor heating.
Engineered timber is the best type of wood flooring to use with floor heating systems as it performs well with changes in floor temperature. Other wood floorings may also be used, but with softer and less dense wood attention must be paid to the thickness of the floorboards, so they do not act as an insulator blocking the heat. As a general rule for wood flooring, the floor surface temperature must not exceed 27°C.
Floor heating changes the moisture content of wood, so special attention must be paid when choosing the wood flooring that can adapt to the changes in floor temperatures without changing the appearance of the floor. Kiln-dried wood tends to work best with floor heating, but always check with the flooring manufacturer about suitability for use with floor heating.
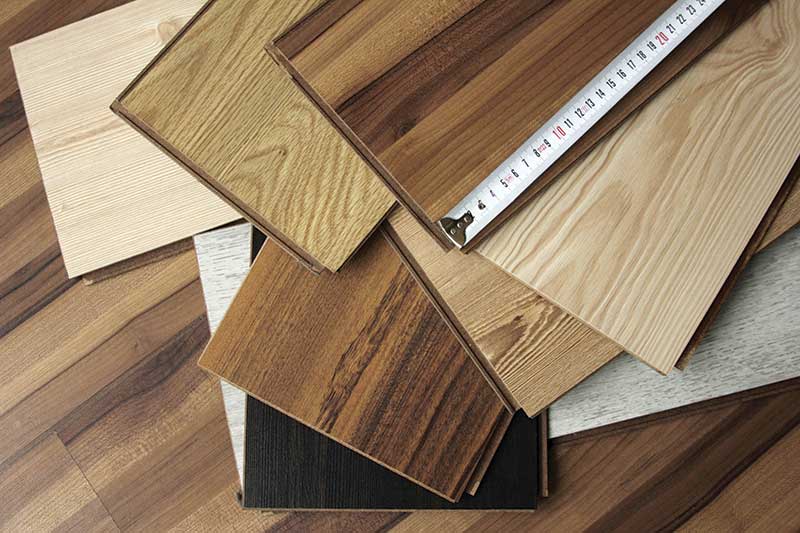

Floor heating can be used with different wood flooring types, but attention must be paid to the thickness of the floor boards so that they do not act as an insulator blocking the heat.
Engineered timber
- The best wood flooring to use with floor heating
- Performs well with the changing floor temperature and adapts to the changing moisture content
Solid hardwood
- Prone to humidity and temperature changes which could result in gapping, cupping and crowning. Care must be taken when considering use with floor heating to ensure compatibility and high enough heat output – always check with the manufacturer about suitability for use with floor heating
Soft woods
- Suitable for use with floor heating, but attention must be paid to the thickness of floor boards to ensure high enough heat output
Parquet floor
- Available in either solid wood or engineered timber and most types are suitable for use with floor heating
Bamboo
- Similar to engineered wood in construction and as it is a good conductor of heat, it is well suited for use with floor heating
Installation tips: floor heating with wood flooring
- Wood is a natural material which is affected by the humidity of the environment around the material. This is why it’s important to ensure the correct moisture content of wood flooring during installation and the correct heating cycle when installing floor heating
- Engineered timber can be laid directly over floor heating with floating floor or batten/joisted system. Boards less than 20mm thick should be supported and fixed to provide suitable structural support. Low tog underlays are recommended when installing the boards over screed
LAMINATE FLOORING
This synthetic floor simulates wood and offers a stain and scratch resistant floor finish. It’s easy to lay and a cost effective solution. Most laminates are suitable for use with floor heating, but it is advisable to check with the flooring manufacturer before installing the system.
VINYL FLOORING
Vinyl flooring can be safely used with floor heating. Vinyl heats up and cools down quickly. Vinyl floors are subject to a top floor temperature restriction, usually 27°C, limiting the heat output so they are not recommended in high heat loss areas.
RUBBER FLOORING
Rubber can be used with floor heating. Solid rubber flooring is usually very conductive making it heat up fast and provide high heat output. Always consult the manufacturer to ensure suitability for use with floor heating.
CARPET FLOORING
Carpet is suitable for use with floor heating, provided that the material of the carpet or underlay does not act as an insulator blocking the heat. The total tog of all materials, including any under and overlays, must not exceed 2,5 tog in order for the system to provide sufficient heat output.

HEAT UP TIMES OF DIFFERENT FLOORS
The choice of flooring material affects the heat up time, as each material has different thermal mass and conductivity. The lower thermal mass and higher the conductivity, the quicker the heat from an floor heating system transfers onto the floor surface. However, this also means that materials with low thermal mass cool down faster than materials with high thermal mass.
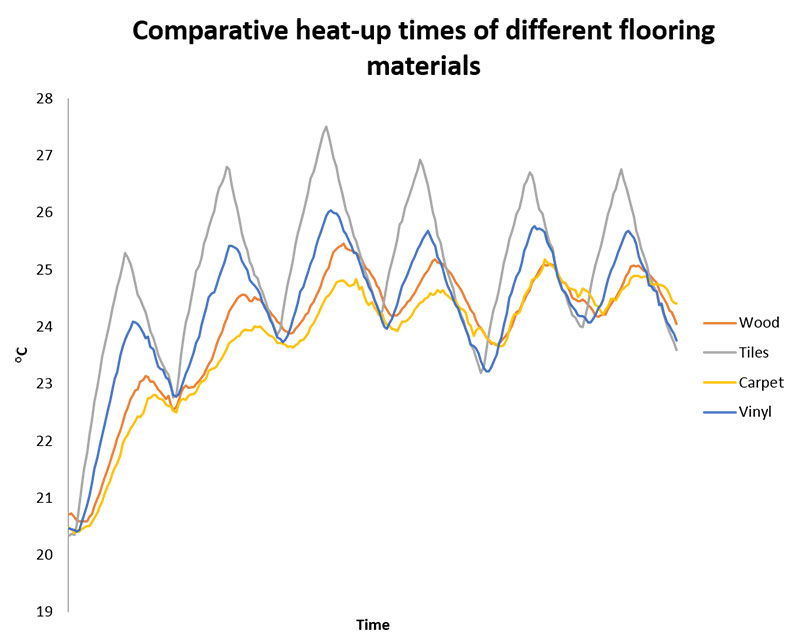
The responsiveness of a system can be improved by using insulation boards to promote the transfer of the heat to the floor finish.
IMPACT ON HEAT OUTPUT
The choice of flooring affects the maximum heat output of the system as certain floor finishes have a top temperature restriction, limiting the maximum heat output. The heat output of a system is dependent on the overall heated floor area and air and floor temperatures. Heat output is influenced by changing any of these three factors. It’s usually the easiest to change the floor finish as the room size and comfort air temperature are already pretty much set.
It’s important to ensure that the heat output from the floor is greater than the heat loss figure of the room. As the graph below illustrates, a two-degree difference in the floor temperature makes a great difference in heat output. So, if the chosen flooring can only be heated to 27°C, and this does not give the heat output required, it might be beneficial to change to a floor finish that can be heated to 29°C to give more heat output. Additionally, adding supplementary heating can be considered to ensure the heating system meets expectations.
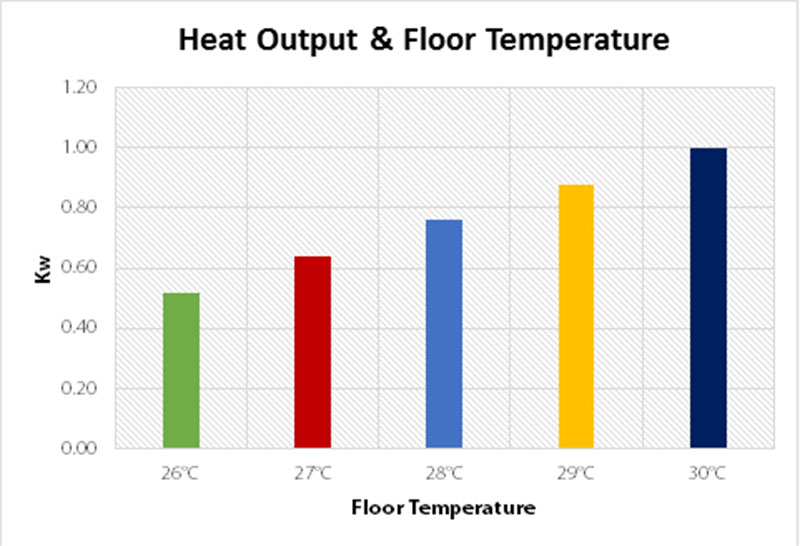
The maximum heat output is directly linked to the floor temperature. The graph illustrates the maximum heat output of a floor heating system when the desired room temperature is 21°C and the heated area is 10m².
Take a look at our product pages to find a system suitable for use with the chosen floor finish.
[ssba]
